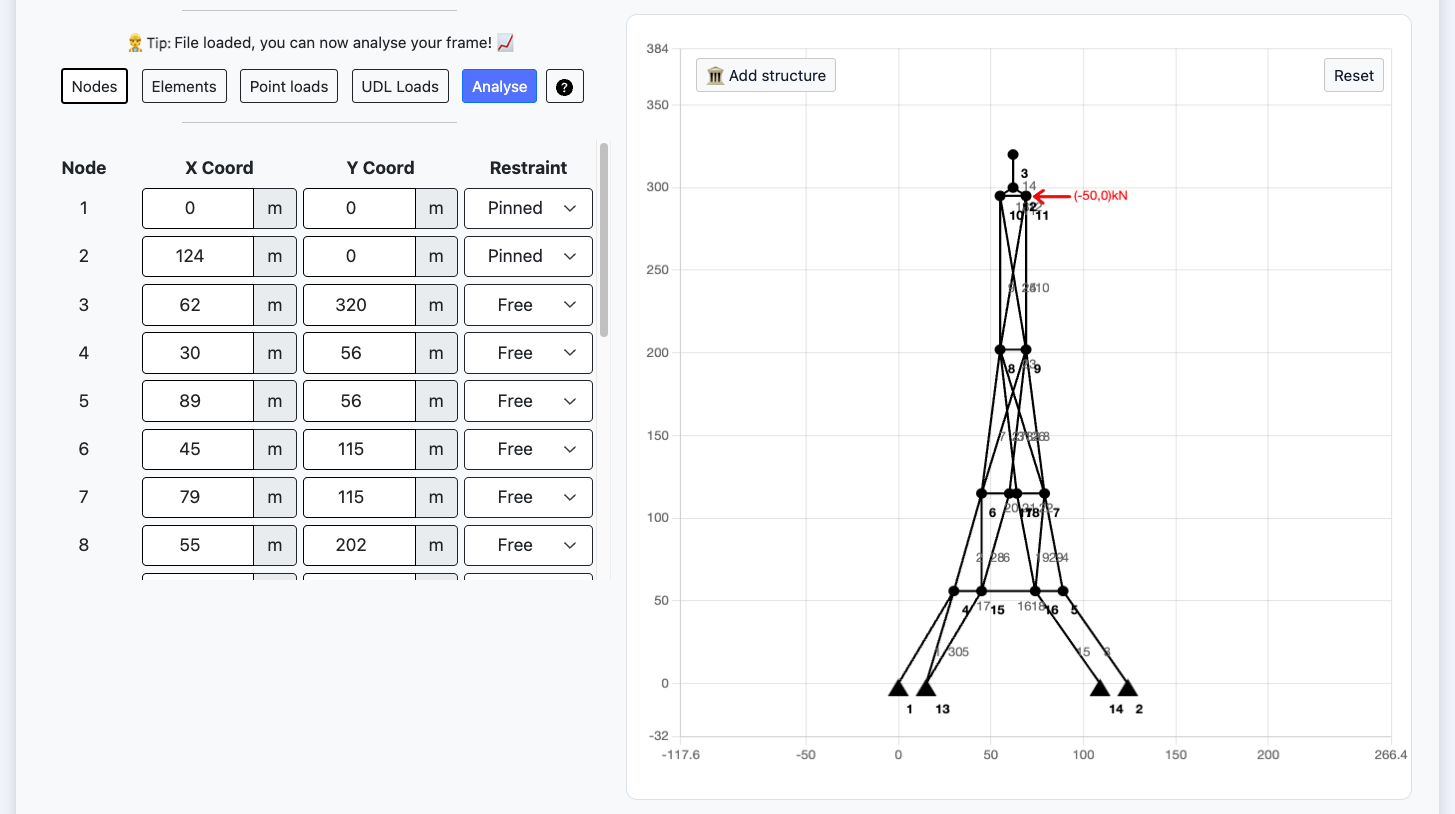
Free Ground Anchors Design Calculator
Design the ground anchors & sheet piles for an underground retaining wall.
Loading...
This analysis uses the Fixed earth approach to resolve the minimum pile toe level, the embedment is increased 20% to provide the fixed earth resultant force.
Loading...
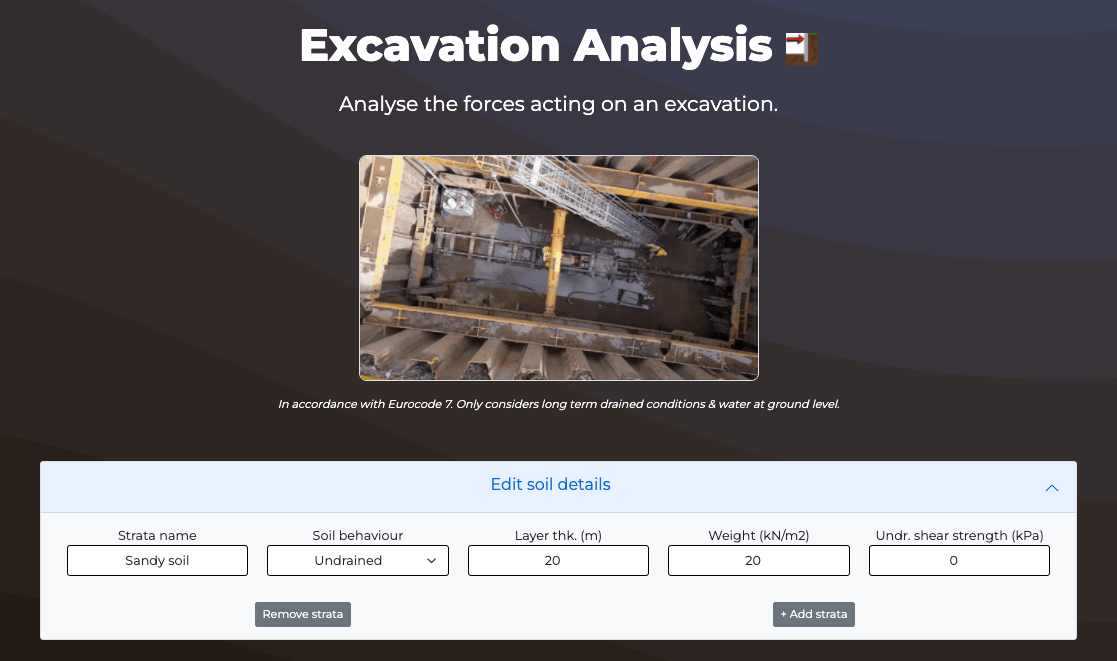
Excavation Design
Anchor depth
m
Check that anchor depth is above excavation depth.
Anchor length
m
Anchor length less than 8m.
Anchor 2 depth
m
Check that anchor depth is above excavation depth.
Anchor 3 depth
m
Check that anchor depth is above excavation depth.
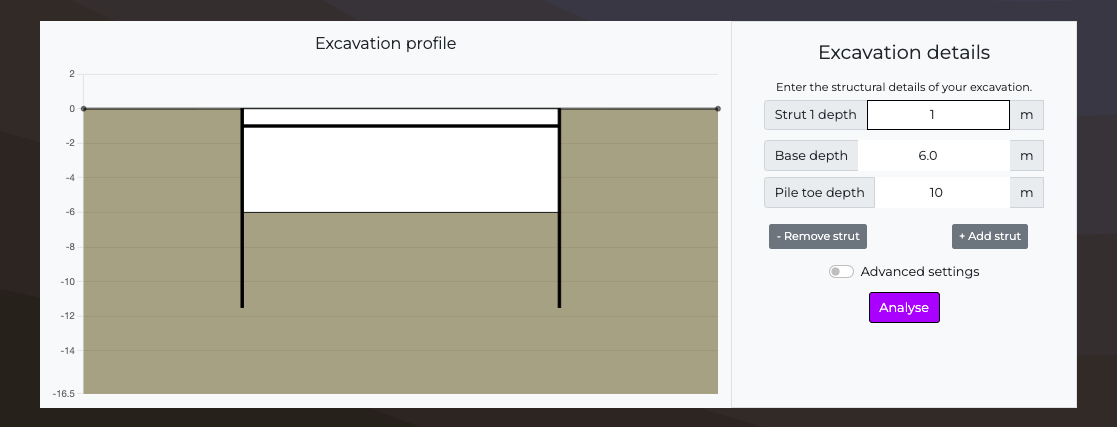
Base depth
m
Check that soil is deep enough, base cannot be deaper than toe, max depth of 30m.
Minimum pile toe depth
m
Max depth of 30m & check that soil is deep enough.
Angle of anchor
o
Advanced settings
Anchor grout details
Select an anchor specification to modify anchor properties.
Anchor grout strength
MPa
Enter a number between 0 and 100.
Anchor grout pressure
kPa
Enter a number between 0 and 2000.
Grout hole diameter
mm
Enter a number greater than reinforcement diameter or 0.
Surcharge details
Include a surcharge alongside the wall
Surcharge
kPa
Enter a number between 0 and 150.
Steel yield strength
N/mm2
Youngs Modulus E
GPa
Enter a number between 0 and 750.
Moment of inertia I
cm4
Enter a number between 0 and 1000000.
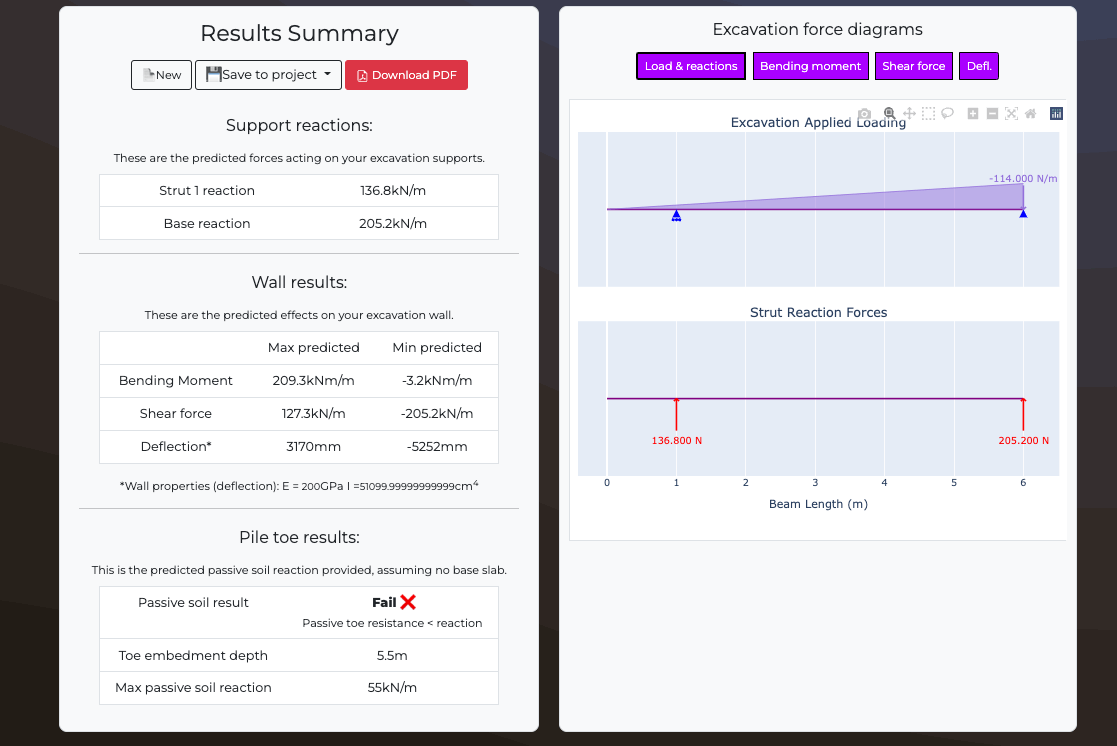
Excavation reactions:
| Char. applied load to anchor | |
| Design applied load to anchor | |
| Max passive soil reaction | |
| Total anchor length | m |
| Free anchor length | m |
| Fixed anchor length | m |
Anchor analysis results:
These are the predicted forces acting on your excavation supports. Anchor capacities are estimated using the Bustamante & Doix (1985) method
Select an anchor specification & we will automatically generate calculations & results here.
Bending Moment Diagram
Shear Force Diagram
Wall Deflection Diagram
This analysis assumes that supporting stuts are rigid and do not act as springs. Stiffness of wall can be modified in advanced settings.
Sheet pile resultant forces:
These are the predicted effects on your sheet pile wall.
| Max predicted | Min predicted | |
| Bending Moment | ||
| Shear force | ||
| Deflection* |
*Wall properties (deflection):
E = GPa
I =cm4
Select a sheet piling size to automatically generate results here
Ground Anchor Design Theory
What are ground anchors?
- A steel bar is inserted through the wall of an excavation and is fixed into the soil or rock either through friction or via a grout. It retains the excavation wall via a waler plate threaded onto the anchor.
What’s the difference between soil nails and ground anchors?
- Although soil nails and ground anchors are very similar, they have a different grouted length. Soil nails are grouted along their full length whereas ground anchors are only grouted along part of their length.
What’s the difference between active and passive ground anchors?
- Active ground anchors are subject to post-tensioning, meaning they require no wall movement to provide restraint. Passive ground anchors are subject to no post-tensioning after installation meaning they required wall movement to start providing resistance.
How are ground anchors designed?
- Design of ground anchors using the Bustamante and Doix (1985) approach considers the strength of the anchor as being the minimum of the steel bar strength, the adhesion between the anchor and the grout block and the adhesion between the grout block and surrounding ground. The strength of the interface between the grout block and ground must only consider the length of the grouted anchor beyond the active earth pressure wedge. Calculation of the strength of the interface between the grout block and steel/grout must also consider that only part of the anchor length is bonded. Ground anchors and soil nails designed with the Bustamante and Doix approach are designed using an empirical approach.

Answer 1: 5.6m
Answer 2: 395kN
What's this calculator used for?
This is a free calculator for Geotechnical Engineers to check the capacity and anchorage of ground anchors against applied earth pressure. This calculator uses the Net Available passive resistance method (Burland) & Eurocode 7. Using this Engineering tool the active earth pressures applied to a retaining wall are calculated. Drained water conditions are used & ground water level is taken as being at ground level.
Contribute to this calculator
This calculator is open-source and you can contribute to it's development.
You can find the source code on GitHub here: PyAnchor
Special credits: Andrea Carigi
Interested in learning more about automation?

Enroll on our training certifications and learn how to code, build AI applications with no-code tools and automate tasks.